Add UNIQUE Constraint to Customer Email
Add UNIQUE Constraint to Customer Email
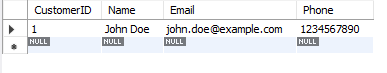
Customer2 Table:
Query Explanation:
-
Creating the Customer2 Table:
-
CREATE TABLE Customer2: This command creates a new table named
Customer2. -
CustomerID INT PRIMARY KEY: Defines the
CustomerIDcolumn as an integer, which is the primary key for theCustomer2table. This means that eachCustomerIDwill be unique. -
Name VARCHAR(100): Defines the
Namecolumn to store the customer's name with a maximum length of 100 characters. -
Email VARCHAR(100): Defines the
Emailcolumn to store the customer's email with a maximum length of 100 characters. -
Phone VARCHAR(15): Defines the
Phonecolumn to store the customer's phone number with a maximum length of 15 characters.
-
-
Adding a UNIQUE Constraint to the Email Column:
-
ALTER TABLE Customer2: Modifies the existing
Customer2table. -
ADD CONSTRAINT unique_email UNIQUE (Email): Adds a
UNIQUEconstraint to theEmailcolumn. This ensures that all email addresses in theEmailcolumn must be unique across all rows in the table. No two customers can have the same email address.
-
-
Inserting Valid Data (Unique Email):
-
INSERT INTO Customer2: This command inserts data into the
Customer2table. -
Values (1, 'John Doe', 'john.doe@example.com', '1234567890'): Inserts a new record for the customer with
CustomerID1,Name'John Doe',Email'john.doe@example.com', andPhone'1234567890'. This operation is valid because the email address is unique.
-
-
Inserting Invalid Data (Duplicate Email):
-
INSERT INTO Customer2: This command attempts to insert another record into the
Customer2table. -
Values (2, 'Jane Smith', 'john.doe@example.com', '9876543210'): Attempts to insert a second customer with the same email
'john.doe@example.com'. Since theEmailcolumn has aUNIQUEconstraint, this operation will fail because email addresses must be unique across all records.
-
-
Error Message:
-
When trying to insert the second record with the duplicate email, the database will return an error
-
SQL Query:
-- Creating Customer2 table
CREATE TABLE Customer2 (
CustomerID INT PRIMARY KEY, -- CustomerID is the primary key for the Customer table.
Name VARCHAR(100), -- Name of the customer.
Email VARCHAR(100), -- Email of the customer.
Phone VARCHAR(15) -- Phone number of the customer.
);
-- Altering the Customer table to add a UNIQUE constraint to the Email column
ALTER TABLE Customer2
ADD CONSTRAINT unique_email UNIQUE (Email); -- Ensuring that Email column values are unique across all customers.
-- Inserting valid data (Unique email)
INSERT INTO Customer2 (CustomerID, Name, Email, Phone)
VALUES (1, 'John Doe', 'john.doe@example.com', '1234567890'); -- A unique email is inserted for this customer.
-- Inserting data with a duplicate email (This will fail)
INSERT INTO Customer2 (CustomerID, Name, Email, Phone)
VALUES (2, 'Jane Smith', 'john.doe@example.com', '9876543210'); -- Duplicate email, which will violate the UNIQUE constraint.
Output:
INSERT INTO Customer2 (CustomerID, Name, Email, Phone) VALUES (2, 'Jane Smith', 'john.doe@example.com', '9876543210') Error Code: 1062. Duplicate entry 'john.doe@example.com' for key 'customer2.unique_email' 0.031 sec

